Multi-JOINs and ASOF JOINs
JOIN是Timeplus的一项关键功能,可将来自不同来源和新鲜度的数据合并到新的数据流中。 有关一般介绍,请参阅 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Join_(SQL)。
流表和维度表联查
在Timeplus中,所有数据都存在于流中,默认的查询模式是流式传输。 流流模式侧重于适合流式处理的最新实时尾部数据。 另一方面,历史重点是以往旧的索引数据,并且优化了大批处理,如太细胞扫描。 当一个查询正在对其运行时,流是默认模式。 要查询流的历史数据,可以使用 table () 函数。
有些典型的情况是,无约束的数据流需要通过连接到相对静态尺寸表来丰富。 Timeplus可以在一个引擎中通过流式到维度表加入来存储流式数据和尺寸表。
示例:
在上述例子中, 来自 device_utils 的数据是一个流,而来自 device_products_info 的数据是历史数据,因为它已经被标记 table() 函数。 对于 device_utils中的每行(新),它都会持续与维度表 device_products_info 中的行连接在一起,并使用产品供应商信息丰富流式数据。
支持三种情况:
流 INNER JOIN 表
INNER JOIN 是最常见的 JOIN,它返回的数据在 JOIN 的两端都有匹配的值。
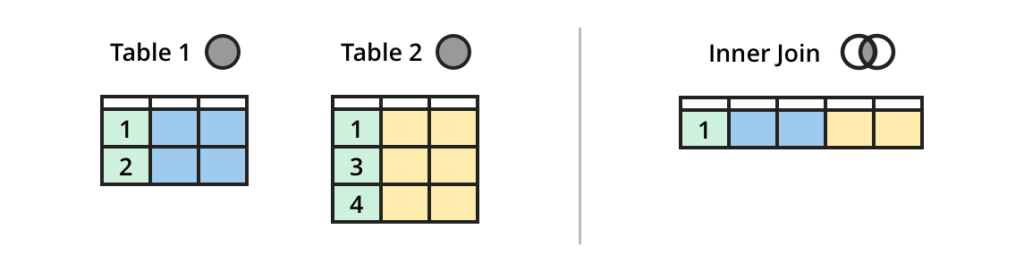
(来源:https://dataschool.com/how-to-teach-people-sql/sql-join-types-explained-visually/)
如果你只使用 JOIN,这也是默认行为。
流 LEFT JOIN 表
LEFT JOIN returns all rows from the left stream with matching rows in the right table. Some columns can be NULL when there is no match. 当没有匹配项时,某些列可能为 NULL。
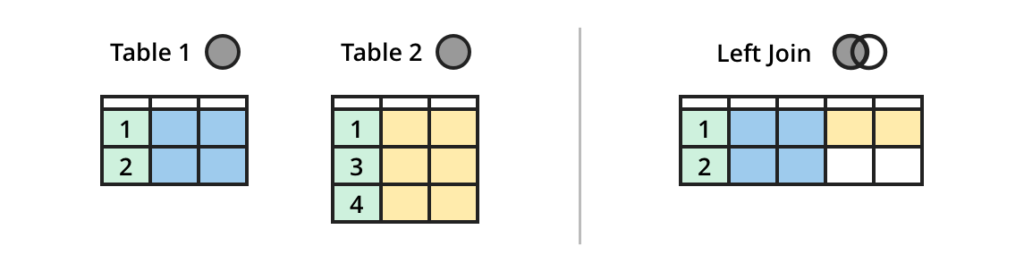
(来源:https://dataschool.com/how-to-teach-people-sql/sql-join-types-explained-visually/)
流 OUTER JOIN 表
OUTER JOIN 合并所有表中的列和行,如果没有匹配项,则包含 NULL。
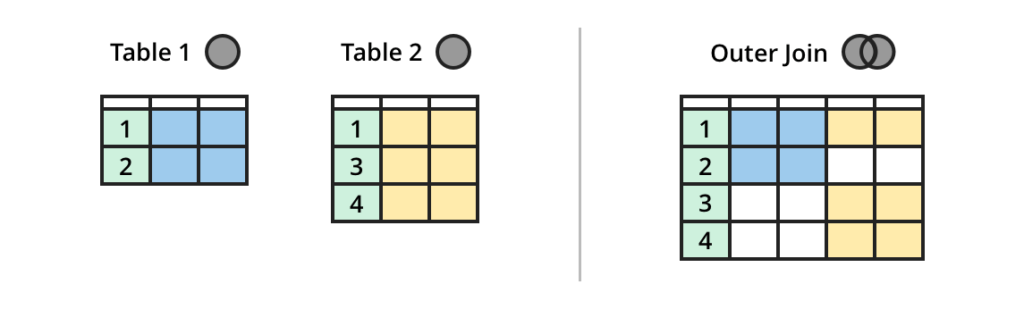
(来源:https://dataschool.com/how-to-teach-people-sql/sql-join-types-explained-visually/)
流到流联查
在某些情况下,实时数据流向多个数据流。 例如,当广告展示给最终用户时,当用户点击广告时。
多个流的相关搜索
Timeplus allows you to do correlated searches for multiple data streams. For example, you can check the average time when the user clicks the ad after it is presented. 例如,您可以查看用户在广告投放后点击广告的平均时间。
Self join
您也可以加入一个流到自己。 一个典型的使用情况是检查同一流中数据是否有某种模式,例如: 是否在两分钟内购买相同的信用卡。 小规模购买后有大宗购买。 这可能是一种欺诈模式。
选择... 选择... 选择... FROM stream1
INNER JOIN stream1 AS stream2
ON stream1.id=stream2.id AND date_diff_within(1m)
WHERE ..
3 种流类型
Timeplus 支持 3 种流类型:
- 仅附加流 (默认)
- Versioned Stream with primary key(s) and multiple versions
- Changelog Stream with primary key(s) and CDC semantic (data can be removed, or updated with old&new value). You can also use the changelog() function to convert an append-only stream to changelog stream. You can also use the changelog() function to convert an append-only stream to changelog stream.
2 种连接类型
1.INNER (default)

(来源:https://dataschool.com/how-to-teach-people-sql/sql-join-types-explained-visually/)
2。向左

(来源:https://dataschool.com/how-to-teach-people-sql/sql-join-types-explained-visually/)
当前版本的 Timeplus 不支持其他类型的连接。 如果你有很好的用例,请通过 support@timeplus.com 联系我们。
- 对
- 全部或外部
- 十字架
4. 严格的JOIN
ALL(默认)LATEST对于两个仅限追加的流,如果你运行a INNER LATEST JOIN b on a.key=b.key,则每当任一流的密钥发生变化时,先前的连接结果将被取消并添加新的结果。ASOF,提供非精确匹配功能。ASOF, provides non-exact matching capabilities. 如果两个流具有相同的id,但时间戳不完全相同,这也可以很好的运作。- 范围
ASOF
支持的组合
简而言之,JOIN 语法是
SELECT <column list>
FROM <left-stream>
[join_type] [join_strictness] JOIN <right-stream>
ON <on-clause>
[WHERE .. 分组依据... 有... 按... 订购]
默认情况下,严格度为 ALL ,连接种类为 INNER。
As you can imagine, there could be 24 (3 x 2 x 4) combinations. Not all of them are meaningful or performant. Please read on for the supported combinations. 并非所有这些都很有意义或性能良好。 请继续阅读支持的组合。
追加加入追加
这可能看起来像是最容易理解的场景。 This may look like the most easy-to-understand scenario. You can try this type of join if you have 2 streams with incoming new data.
但是,这仅用于勘探目的,不建议用于生产用途。 由于数据流的两端都是无限的,因此它将消耗系统中越来越多的资源。 内部设置了最大缓存字节数,以控制其可以缓冲的最大源数据。 一旦查询达到限制,流式查询将中止。
示例:
SELECT * FROM
left_append JOIN right_append
ON left_append.k = right_append.kk
range join append streams
上述联接可能会缓冲过多的数据,范围双向联接试图通过在时间范围内对流数据进行存储桶来缓解此问题,并尝试将数据双向加入到适当的范围存储桶中。 The above join may buffer too much data, range bidirectional join tries to mitigate this problem by bucketing the stream data in time ranges and try to join the data bidirectionally in appropriate range buckets. It requires a date_diff_within clause in the join condition and the general form of the syntax is like below.
SELECT * FROM left_stream JOIN right_stream
ON left_stream.key = right_stream.key AND date_diff_within(2m)
Actually we don’t even require a timestamp for the range, any integral columns are supposed to work. For instance, AND left_stream.sequence_number < rightstream.sequence_number + 10. 例如, 和 left_stream.sequence_number < rightstream.sequence_number + 10。
版本 JOIN 版本
这是 Timeplus 的一项独特功能。 This is a unique feature in Timeplus. You can setup Versioned Stream with data in Kafka or other streaming sources. Assign primary key(s) and join multiple versioned stream, as if they are in OLTP. Whenever there are new updates to either side of the JOIN, new result will be emitted. 分配主密钥并加入多个版本流,就好像它们在 OLTP 中一样。 每当JOIN的两端有新的更新时,都会发出新的结果。
示例:
SELECT k, count(*), min(i), max(i), avg(i), min(ii), max(ii), avg(ii)
FROM left_vk JOIN right_vk
ON left_vk.k = right_vk.kk
追加 INNER JOIN 版本号
这种类型的联接和以下类型使您能够动态丰富数据。 与传统数据库相比,动态数据丰富连接也具有特殊的语义,因为我们不为左流缓冲任何源数据,而是让它继续流动。 This type of join and the following types enable you to dynamic data enrichment. Dynamic data enrichment join has special semantics as well compared to traditional databases since we don’t buffer any source data for the left stream, we let it keep flowing. It is similar to stream to dimension table join, but the difference is we build a hash table for the right stream and dynamically update the hash table according to the join strictness semantics.
示例:
append LEFT JOIN 版本为版本
与上述类似,但将显示仅追加流中的所有行,如果没有匹配项,则版本化流中的列中将显示空值。
示例:
追加 INNER JOIN 变更日志
示例:
追加 LEFT JOIN 变更日志
示例:
追加 ASOF JOIN 版本控制
ASOF 丰富联接在哈希表中保留 相同联接密钥 的多个版本的值,这些值按 ASOF 不等联接密钥排序。
示例:
SELECT * FROM append ASOF JOIN versioned_kv
ON append.k = versioned_kv.k AND append.i <= versioned_kv.j
There is an optional setting to ask the query engine to keep the last N versions of the value for the same join key. 示例: 示例:
SELECT * FROM append ASOF JOIN versioned_kv
ON append.k = versioned_kv.k AND append.i <= versioned_kv.j
SETTINGS keep_versions = 3
向左追加 ASOF JOIN 版本控制
与上面类似,但不是 INNER。
示例:
SELECT * FROM append LEFT ASOF JOIN versioned_kv
ON append.k = versioned_kv.k AND append.i <= versioned_kv.j
追加最新加入版本
Only the latest version of value for each join key is kept. 示例: 示例:
SELECT *, _tp_delta FROM append ASOF LATEST JOIN versioned_kv
ON append.k = versioned_kv.k
然后,您可以向两个流中添加一些事件。
| 添加数据 | SQL 结果 |
|---|---|
向 append 添加一个事件 (id=100,name=apple) | 没有结果 |
向 versioned_kv (id=100,amount=100) 添加一个事件 | 1. id=100, name=apple, amount=100, _tp_delta = 1 |
向 versioned_kv (id=100,amount=200) 添加一个事件 | (新增2 行) 2. id=100, name=apple, amount=100,_tp_delta =-1 3. id=100, name=apple, amount=200,_tp_delta = 1 |
Add one event to append (id=100, name =appl) | (新增2 行) 4. id=100, name =apple, amount=200, _tp_delta =-1 5. id=100, name =appl, amount=200,_tp_delta = 1 |
如果您运行一个聚合函数,使用这种LATEST JOIN, 比如 count(*) 结果将永远是1,无论同一键值有多少次变化。
向左追加最新加入版本
与上面类似,但不是 INNER。
示例:
SELECT * FROM append LEFT LATEST JOIN versioned_kv
ON append.k = versioned_kv.k
版本向左加入版本
此功能在 Proton 1.5.7 中启用。 This is a unique feature in Timeplus. You can setup Versioned Stream with data in Kafka or other streaming sources. Assign primary key(s) and join multiple versioned stream, as if they are in OLTP. Whenever there are new updates to either side of the JOIN, new result will be emitted. 分配主密钥并加入多个版本流,就好像它们在 OLTP 中一样。 每当JOIN的任一端有新的更新时,都会发出新的结果,并且可以将其具体化到目标系统,例如ClickHouse。
示例:
SELECT k, count(*), min(i), max(i), avg(i), min(ii), max(ii), avg(ii)
FROM left_vk LEFT JOIN right_vk
ON left_vk.k = right_vk.kk