High Availability
In a cluster deployment, Timeplus Materialized Views support two high availability (HA) models: Raft-based and Centralized Scheduler-based.
The chosen HA model is tightly coupled with the underlying checkpoint replication strategy, and each comes with its own trade-offs depending on the workload.
Raft-Based HA
The Raft-based HA model is the default option. When you create a Materialized View with this model, Timeplus places three replicas of it on different nodes in the cluster. One replica is elected as the leader and handles the query execution, while the other two act as followers. The leader continuously checkpoints the query state, and these checkpoints are replicated to the followers using the Raft consensus protocol. This ensures that the followers have identical state information, which is crucial for a fast and reliable failover.
Internally, this model leverages a NativeLog checkpoint shard, which is replicated using Raft for fault tolerance.
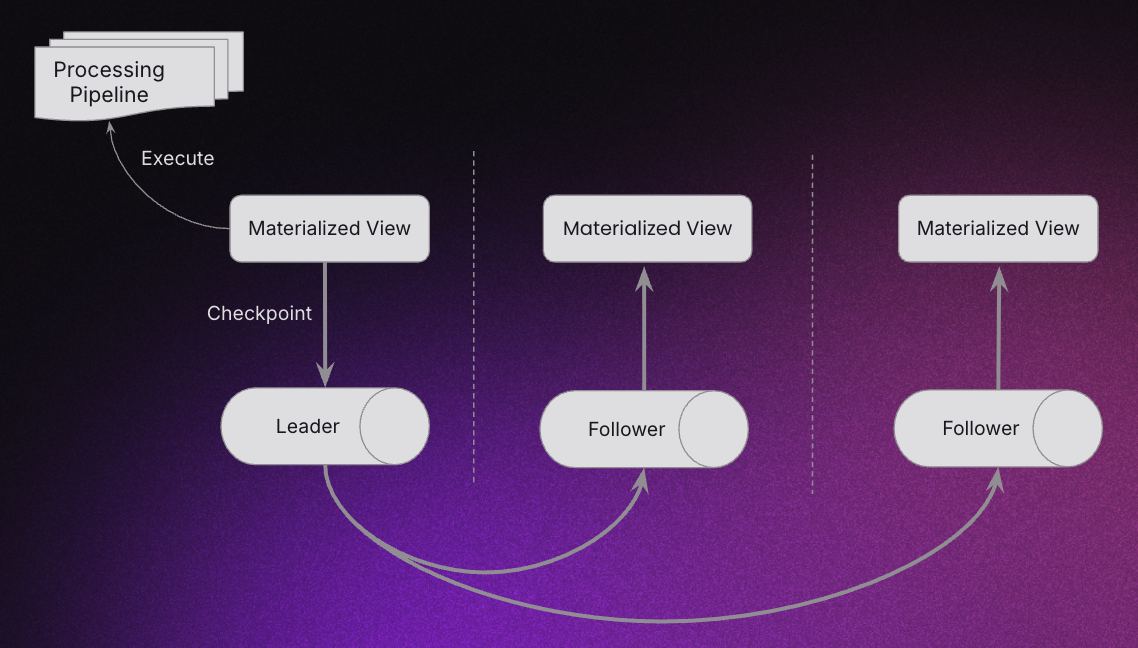
Initial Leader Election
When a Materialized View with this model is created, the following things happen:
- The placement strategy picks three nodes in the cluster.
- A NativeLog shard is provisioned across these three nodes, forming a Raft group.
- One shard replica is elected as the leader and the remaining replicas as followers.
- The leader builds the processing pipeline DAG, executes the query, and writes results.
- The leader periodically checkpoints query state to NativeLog, which replicates to followers. Followers maintain identical state for failover readiness.
Failover
Failure detection and failover are handled automatically by the Raft consensus mechanism.
- If the leader fails or disconnects, a follower is elected as the new leader.
- The new leader rebuilds the pipeline and recovers from the replicated checkpoint.
- Query execution resumes with minimal interruption.
Scheduler-Based HA
In this model, a centralized scheduler monitors Materialized Views and reschedules them on failure. The scheduler itself is Raft-backed, and its leader coordinates placement and recovery.
This model will be selected when creating a Materialized View with these settings:
SETTINGS checkpoint_settings='replication_type=shared;shared_disk=...'
We call this a Scheduled Materialized View, since it is governed by the scheduler.
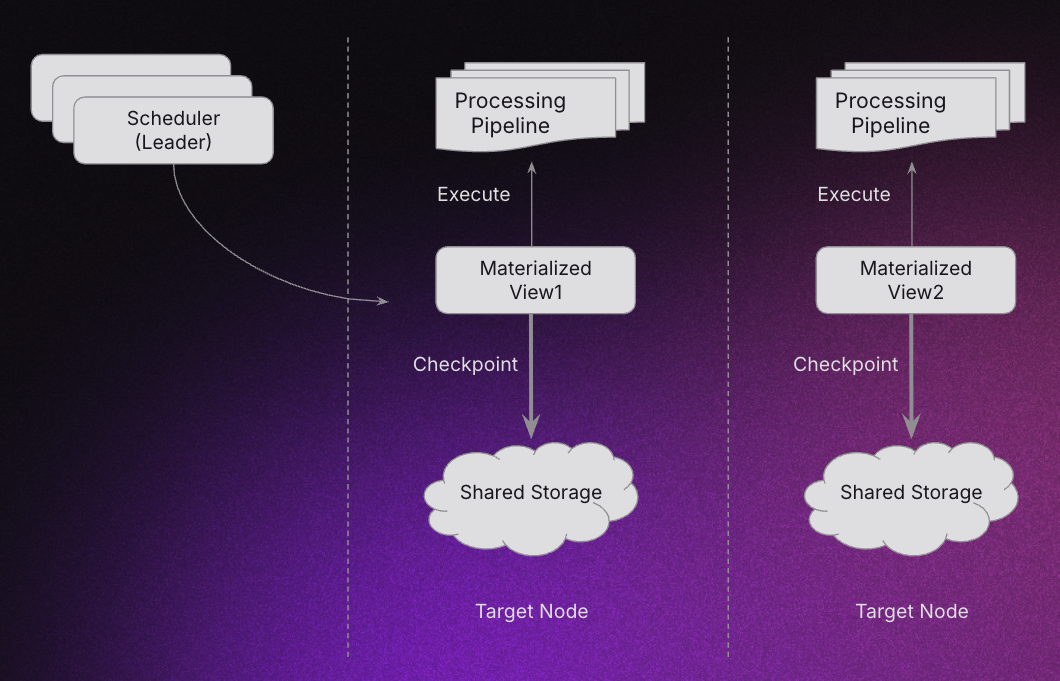
Initial Placement
When a scheduled Materialized View is initially created, the following things happens:
- The scheduler leader selects the best node based on cluster ndoe statistics.
- The chosen node runs the Materialized View.
- The Materialized View commits checkpoints to shared storage according to its schedule.
- The scheduler continuouly monitors node health via heartbeats
Failover
Fault tolerance are two layers in this model.
- If the Materialized View itself fails, the node restarts it locally.
- If the node fails/offlines, the scheduler detects the missed heartbeats.
- The scheduler reschedules all Materialized Views from the failed node to healthy ones.
- Rescheduled views recover state from shared storage and resume execution.
This model integrates well with Kubernetes HPA and AWS Auto Scaling Groups since the Materialized Views don't own any state themselves, supporting highly elastic workloads running on Timeplus Compute Nodes.
Choosing the Right HA Model
Raft-Based HA
Best for:
- On-prem deployments without shared storage (only option).
- Workloads requiring low failover latency.
- Use scenarios where autonomous failover per-maerialized view is desirable.
Trade-offs:
- More expensive (requires multiple hot standby replicas).
- Higher disk space and IOPS usage.
Scheduler-Based HA
Best for:
- Large-scale or spiky workloads with many Materialized Views.
- Use scenarios requiring elasticity and auto-scaling (K8s, cloud autoscaling).
- Lower resource overhead (single replica per view).
Trade-offs:
- Failover can be slower (many Materialized Views may need rescheduling because of one node failure, recovery from shared storage is slower than local).
- Scheduler is a central point of coordination and potential bottleneck.
Recommendation
- For moderate, steady workloads and fast failover, choose Raft-based HA.
- Use NativeLog + Shared Storage checkpoint replication if applicable.
- For large, dynamic, or elastic workloads, choose Centralized Scheduler-based HA.